Soil Degradation: A Threat to Environmental Sustainability
Soil degradation, a widespread and alarming issue, poses a significant threat to global food security and environmental sustainability. As the foundation of agricultural productivity, soil provides essential nutrients, water retention, and a habitat for countless organisms. However, unsustainable land management practices, deforestation, intensive agriculture, and climate change have accelerated soil degradation processes. This article delves into the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to combat soil degradation, highlighting the urgent need for action.
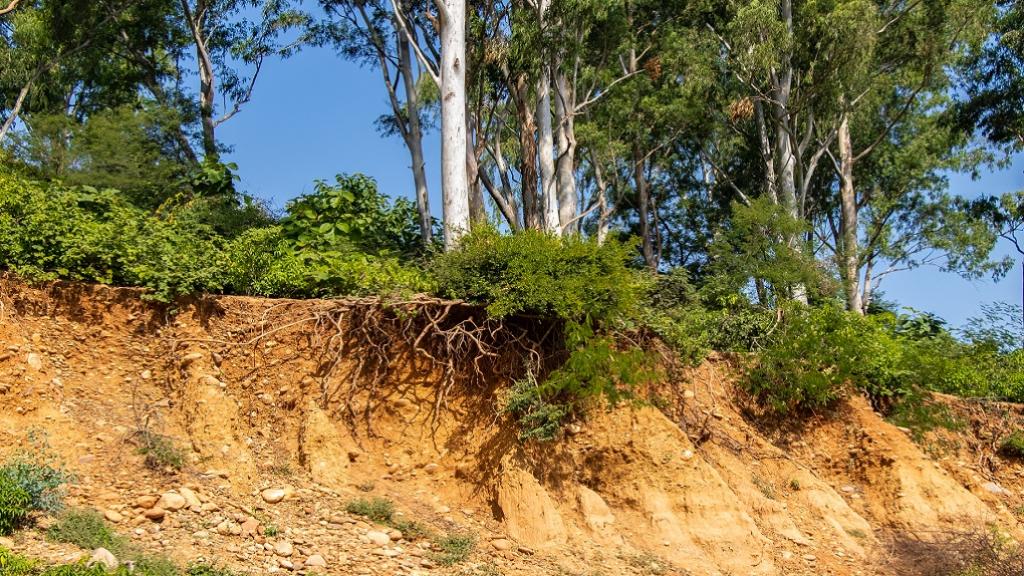

Causes of soil degradation
Erosion
Soil erosion, both water and wind-induced, is a major contributor to soil degradation. Improper land management practices, such as overgrazing, deforestation, and improper plowing techniques, leave soil vulnerable to erosion. The loss of fertile topsoil reduces agricultural productivity and depletes essential nutrients.
Chemical intensive agriculture
The excessive use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides in modern agriculture has detrimental effects on soil health. These practices disrupt the natural balance of soil ecosystems, degrade soil structure, and diminish microbial diversity, leading to decreased nutrient availability and increased vulnerability to erosion.
Deforestation and land conversion
The clearance of forests for agriculture or urbanization disrupts the delicate equilibrium of ecosystems. Without the protective cover of vegetation, soils are exposed to erosion, nutrient depletion, and increased vulnerability to droughts and floods.
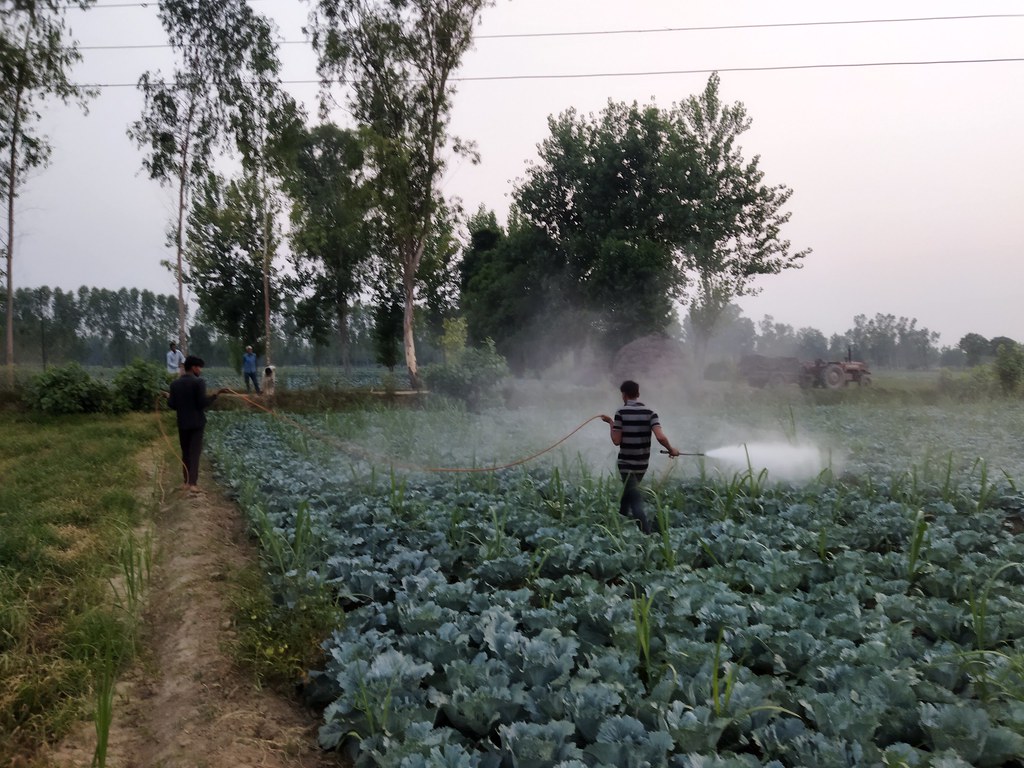

Consequences of soil degradation
Declining agricultural productivity
Soil degradation directly impacts agricultural productivity, leading to reduced crop yields and lower-quality harvests. Nutrient depletion, decreased water retention capacity, and loss of soil structure compromise the ability of plants to grow and thrive, threatening global food security.
Increased Environmental Vulnerability
Degraded soil is more susceptible to environmental challenges, such as water scarcity, droughts, and floods. Soil degradation exacerbates the impacts of climate change, as degraded soils are less resilient to extreme weather events, compromising ecosystem stability and biodiversity.
Soil Health and Human Health Connection
Soil degradation can indirectly affect human health through its impact on food quality and safety. Nutrient deficiencies in crops grown in degraded soils can lead to nutritional imbalances in diets, affecting human health and exacerbating food insecurity.
Solutions to Combat Soil Degradation
Sustainable Land Management Practices
Implementing sustainable land management practices such as conservation agriculture, agroforestry, and organic farming, helps mitigate soil degradation. These practices promote soil conservation, enhance organic matter content, improve water retention capacity, and reduce erosion risks.
Soil Conservation Techniques
Implementing soil conservation techniques like contour plowing, terracing, and reforestation helps prevent erosion and improve soil structure. Conservation measures, such as cover cropping, crop rotation, and the use of organic fertilizers, contribute to soil fertility and enhance overall soil health.
Policy Support and Awareness
Governments and international organizations play a crucial role in promoting policies and regulations that incentivize sustainable land management practices. Increasing awareness among farmers, stakeholders, and consumers about the importance of soil conservation and sustainable agriculture can drive the adoption of responsible practices.

Wrap up
Soil degradation poses a formidable challenge to food security, environmental sustainability, and human well-being. Urgent action is needed to address the root causes of soil degradation and promote sustainable land management practices. By adopting soil conservation techniques, implementing sustainable farming practices, and raising awareness about the importance of soil health, we can restore and protect our soils, ensuring a resilient and productive agricultural system for present and future generations.


